Jan 13, 2026 2:09 PM
More Trump-Kennedy Center Cancellations
The fallout from the renaming of the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts to include President Donald…

The results of Epitaph are alternately lyrical, cacophonous, raucous and elegiac.
(Photo: Jan Persson)Any consideration of Charles Mingus’ corpus must contend with Epitaph, his magnum opus, a monster orchestral work that is, like the man himself, ambitious, sprawling, ungainly, virtuosic, overstuffed, angry, passionate and restless. Consisting of 19 movements, it was written for an orchestra of 31 — in effect a double big band, augmented by bassoon, oboe, tuba, timpani, electric guitar and vibes.
The score, which exceeds 500 pages, was written over a 20-year period. It takes more than two hours to perform, and was painstakingly pieced together after his death in 1979 by musicologist Andrew Homzy, who found it in the home of Sue Mingus, Mingus’ wife. She had asked Homzy to catalogue the Mingus papers, now residing in the Library of Congress.
Ultimately unclassifiable, it can be construed as a postmodern take on traditional and modern jazz as well as European classical forms and conventions. It includes a few of his best-known works, “Better Get It In Your Soul,” “Peggy’s Blue Skylight,” and “Freedom,” throwbacks to early jazz (Jelly Roll Morton’s “Wolverine Blues”) and nods to Duke Ellington and Thleonious Monk. The work constantly confounds expectations; any time it threatens to go somewhere conventionally, it reaches for the unexpected. The results are alternately lyrical, cacophonous, raucous and elegiac.
Epitaph rose like a phoenix — eventually — from the ruins of what Mingus considered his biggest failure: his disastrous 1962 concert at New York’s Town Hall. The huge orchestra — which included Snooky Young and Clark Terry on trumpets and Eric Dolphy, Charles McPherson and Zoot Sims on saxophones, among many other greats — had been assembled but never properly rehearsed. Copyists were still madly scribbling parts even as the concert was underway. There was even disagreement between the promoters (including George Wein) and Mingus about how to describe the event: Mingus wanted a public recording session, but advertising called it a concert. At one point, according to multiple accounts, Mingus grabbed the mic and exhorted the audience to ask for its money back.
The work was later championed by Gunther Schuller, who conducted the first complete concert version at Lincoln Center in 1989 with a band that included Wynton Marsalis, Snooky Young and Randy Brecker on trumpets, and George Adams and John Handy on saxophones. Sony/Columbia released the recording as a double album the following year. Schuller oversaw another version in 2007, which played in New York, Chicago, Cleveland and Los Angeles with Christian McBride on bass.
Musicians who have performed it testify to its difficulty. Marsalis is said to have once pointed at a passage in the score, saying, “That looks like something you would find in an etude book ... under ‘hard.’”
As you might expect, the bass is often front and center. McBride, recalling the experience, said, “I didn’t get too hung up on the technical difficulty. Any passage I had problems with — well, you just have to practice harder. [But] my sense was that he didn’t want it perfect.” DB
Belá Fleck during an interview with Fredrika Whitfield on CNN.
Jan 13, 2026 2:09 PM
The fallout from the renaming of the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts to include President Donald…
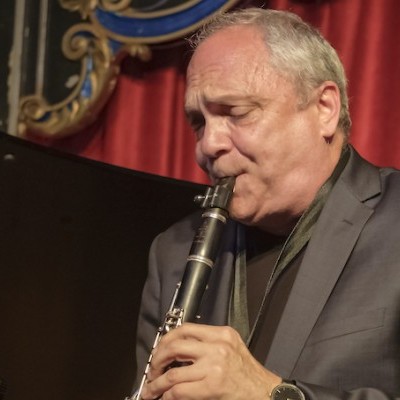

Peplowski first came to prominence in legacy swing bands, including the final iteration of the Benny Goodman Orchestra, before beginning a solo career in the late 1980s.
Feb 3, 2026 12:10 AM
Ken Peplowski, a clarinetist and tenor saxophonist who straddled the worlds of traditional and modern jazz, died Feb. 2…
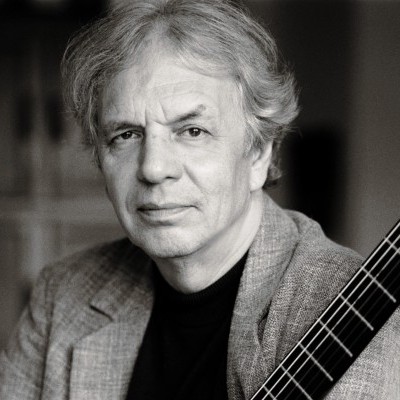

The success of Oregon’s first album, 1971’s Music Of Another Present Era, allowed Towner to establish a solo career.
Jan 19, 2026 5:02 PM
Ralph Towner, a guitarist and composer who blended multiple genres, including jazz — and throughout them all remained…
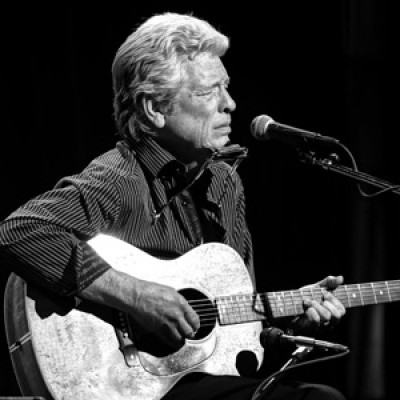

Hammond came to the blues through the folk boom of the late 1950s and early 1960s, which he experienced firsthand in New York’s Greenwich Village.
Mar 2, 2026 9:58 PM
John P. Hammond (aka John Hammond Jr.), a blues guitarist and singer who was one of the first white American…

Rico’s Anti-Microbial Instrument Swab
Jan 19, 2026 2:48 PM
With this year’s NAMM Show right around the corner, we can look forward to plenty of new and innovative instruments…