Jan 13, 2026 2:09 PM
More Trump-Kennedy Center Cancellations
The fallout from the renaming of the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts to include President Donald…

Quincy Jones once described Ernestine Anderson’s voice as the “sound of honey at dusk.”
It was an accurate, evocative description of a vocalist whose career spanned six decades, including a performance at the first Monterey Jazz Festival in 1958, four Grammy nominations and a spot in the Smithsonian Institution’s “Jazz Singers” anthology. Anderson died March 10, at age 87.
Born in 1928, in Houston, Anderson began her professional career when she was 12, after winning a talent contest at Houston’s Eldorado Ballroom. She often said that this experience—which forced her to improvise because she gave the pianist the wrong key—made her realize she was a jazz singer.
In 1944, Anderson’s family moved to Seattle, where she became a fixture on Jackson Street’s after-hours scene, which included Jones, bassist Buddy Catlett and, later, Ray Charles. In 1947, Anderson went out on the road with Los Angeles r&b bandleader Johnny Otis.
“She was out with Johnny Otis and those bands before anybody,” Jones said. “Everyone was in awe of anybody that had gone on the road with a professional band.”
When Otis disbanded the group in Los Angeles, Anderson remained there, recording her first single, “K.C. Lover/Good Lovin’ Babe,” for the Black & White label. In 1952, she began a 15-month tour with Lionel Hampton, whose band at that time included Jones, trumpeter Clifford Brown and alto saxophonist Pony Poindexter and performed at the presidential inauguration of Dwight D. Eisenhower.
Moving to New York, Anderson worked at the Page Three, a nightclub where Sheila Jordan also sang. In 1955, Anderson appeared on two tracks of an album by alto saxophonist Gigi Gryce, Nica’s Tempo, which also featured trumpeter Art Farmer, with whom she later lived for several years.
The following year, Anderson went to Europe, where she recorded with bandleader Harry Arnold for the Metronome label. Championed by San Francisco jazz critic Ralph J. Gleason, Anderson’s album was picked up by Mercury and released in 1958. Hot Cargo netted rave reviews in Time magazine and The New York Times, where critic John S. Wilson compared her to Ella Fitzgerald, though her inspiration was Sarah Vaughan. Anderson’s singing was elegant and pure, with fastidious diction, and she swung effortlessly. The following year, she was toasted by DownBeat as a “new star.”
Anderson released six albums on Mercury. One of the best was Moanin’, Moanin’, Moanin, with its knockout version of “Come Rain Or Come Shine.” But by 1966, with the rock revolution in full swing, Anderson’s star fell and she retired from music.
Three years later, while living in L.A., she discovered Buddhist chanting, which she credited with lifting her out of a severe depression. In 1973, she was coaxed back to performing by Seattle jazz critic Maggie Hawthorn. Eventually managed by Ray Brown, Anderson signed with Concord Jazz. Hello, Like Before came out in 1977 and was followed by more than a dozen albums over the next 15 years, as well as tours in Japan, South America and Europe.
Singing in a more world-wise, raspier and blues-oriented style, Anderson took as her signature song a finger-popping blues recorded by B.B. King, “Never Make Your Move Too Soon.” During this period, Anderson could also still ring the bells of standard ballads like “Skylark” and “Old Folks.”
Anderson left Concord in 1993 and signed to Jones’ label, Qwest, which presented her in a soul-jazz mode, netting Grammy nominations and strong sales for Now And Then (1993) and Blues, Dues & Love News (1996).
Never a bestselling artist, Anderson was consistently praised by critics and was making well-reviewed albums after 2000. In 2015, High Note released a 1962 live recording from Seattle’s Penthouse nightclub, Ernestine Anderson Swings The Penthouse. The album was a keen reminder of how pure and moving Anderson’s voice had been in her early career.
Belá Fleck during an interview with Fredrika Whitfield on CNN.
Jan 13, 2026 2:09 PM
The fallout from the renaming of the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts to include President Donald…
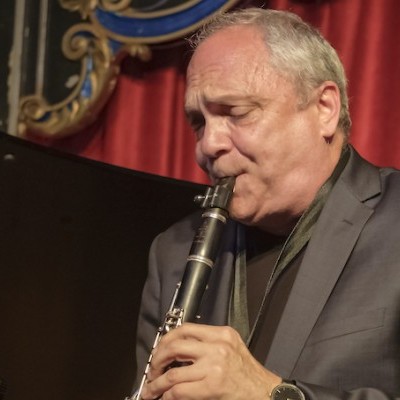

Peplowski first came to prominence in legacy swing bands, including the final iteration of the Benny Goodman Orchestra, before beginning a solo career in the late 1980s.
Feb 3, 2026 12:10 AM
Ken Peplowski, a clarinetist and tenor saxophonist who straddled the worlds of traditional and modern jazz, died Feb. 2…
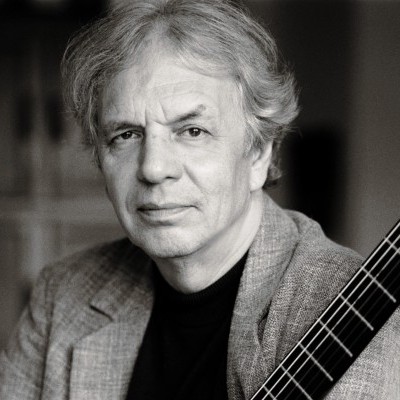

The success of Oregon’s first album, 1971’s Music Of Another Present Era, allowed Towner to establish a solo career.
Jan 19, 2026 5:02 PM
Ralph Towner, a guitarist and composer who blended multiple genres, including jazz — and throughout them all remained…

Rico’s Anti-Microbial Instrument Swab
Jan 19, 2026 2:48 PM
With this year’s NAMM Show right around the corner, we can look forward to plenty of new and innovative instruments…
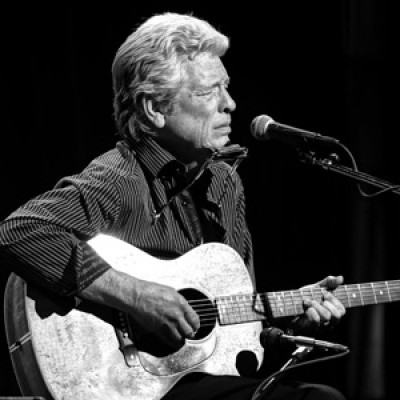

Hammond came to the blues through the folk boom of the late 1950s and early 1960s, which he experienced firsthand in New York’s Greenwich Village.
Mar 2, 2026 9:58 PM
John P. Hammond (aka John Hammond Jr.), a blues guitarist and singer who was one of the first white American…